Mechanical pumps may be submerged in the fluid they are pumping or be placed external to the fluid.
Pumps can be classified by their method of displacement into positive-displacement pumps, impulse pumps, velocity pumps, gravity pumps, steam pumps and valveless pumps. There are three basic types of pumps: positive-displacement, centrifugal and axial-flow pumps. In centrifugal pumps the direction of flow of the fluid changes by ninety degrees as it flows over an impeller, while in axial flow pumps the direction of flow is unchanged.
Positive-displacement pumps
Positive-displacement pump behavior and safety
Positive-displacement pumps, unlike centrifugal, can theoretically produce the same flow at a given speed (rpm) no matter what the discharge pressure. Thus, positive-displacement pumps are constant flow machines. However, a slight increase in internal leakage as the pressure increases prevents a truly constant flow rate.
A positive-displacement pump must not operate against a closed valve on the discharge side of the pump, because it has no shutoff head like centrifugal pumps. A positive-displacement pump operating against a closed discharge valve continues to produce flow and the pressure in the discharge line increases until the line bursts, the pump is severely damaged, or both.
Positive-displacement types
A positive-displacement pump can be further classified according to the mechanism used to move the fluid:
- Rotary-type positive displacement: internal or external gear pump, screw pump, lobe pump, shuttle block, flexible vane or sliding vane, circumferential piston, flexible impeller, helical twisted roots (e.g. the Wendelkolben pump) or liquid-ring pumps
- Reciprocating-type positive displacement: piston pumps, plunger pumps or diaphragm pumps
- Linear-type positive displacement: rope pumps and chain pumps
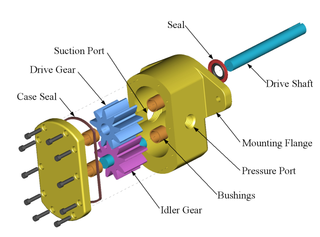 A gear pump uses the meshing of gears to pump fluid by displacement. They are one of the most common types of pumps for hydraulic fluid power applications. The gear pump was invented around of year 1600.
A gear pump uses the meshing of gears to pump fluid by displacement. They are one of the most common types of pumps for hydraulic fluid power applications. The gear pump was invented around of year 1600.
Gear pumps are also widely used in chemical installations to pump high viscosity fluids. There are two main variations: external gear pumps which use two external spur gears, and internal gear pumps which use an external and an internal spur gear (internal spur gear teeth face inwards, see below). Gear pumps are positive displacement (or fixed displacement), meaning they pump a constant amount of fluid for each revolution. Some gear pumps are designed to function as either a motor or a pump.
As the gears rotate they separate on the intake side of the pump, creating a void and suction which is filled by fluid. The fluid is carried by the gears to the discharge side of the pump, where the meshing of the gears displaces the fluid. The mechanical clearances are small— in the order of 10 μm. The tight clearances, along with the speed of rotation, effectively prevent the fluid from leaking backwards.
The rigid design of the gears and houses allow for very high pressures and the ability to pump highly viscous fluids.
Many variations exist, including helical and herringbone gear sets (instead of spur gears), lobe shaped rotors similar to Roots blowers (commonly used as superchargers), and mechanical designs that allow the stacking of pumps. The most common variations are shown below (the drive gear is shown blue and the idler is shown purple).
 Applications
Applications
- Petrochemicals: Pure or filled bitumen, pitch, diesel oil, crude oil, lube oil etc.
- Chemicals: Sodium silicate, acids, plastics, mixed chemicals, isocyanates etc.
- Paint and ink.
- Resins and adhesives.
- Pulp and paper: acid, soap, lye, black liquor, kaolin, lime, latex, sludge etc.
- Food: Chocolate, cacao butter, fillers, sugar, vegetable fats and oils, molasses, animal food etc.
Rotary positive-displacement pumps fall into 5 main types:
- Gear pumps – a simple type of rotary pump where the liquid is pushed around a pair of gears.
- Screw pumps – the shape of the internals of this pump is usually two screws turning against each other to pump the liquid
- Rotary vane pumps
- Hollow disk pumps (also known as eccentric disc pumps or Hollow rotary disc pumps).
- Vibratory pumps or vibration pumps




















